AlphaDog

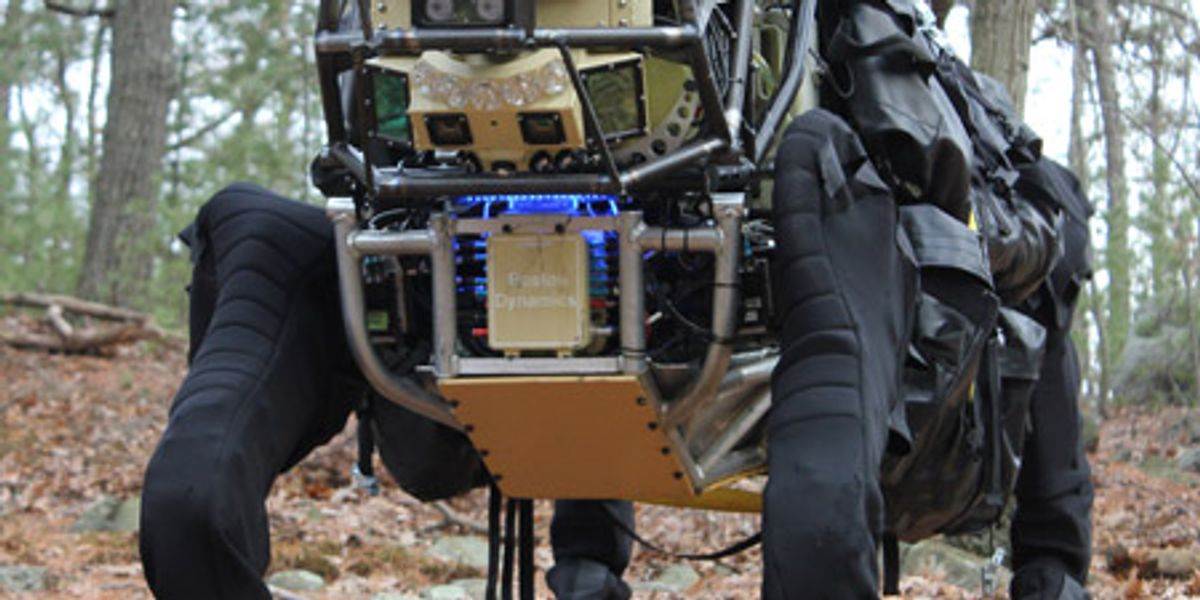
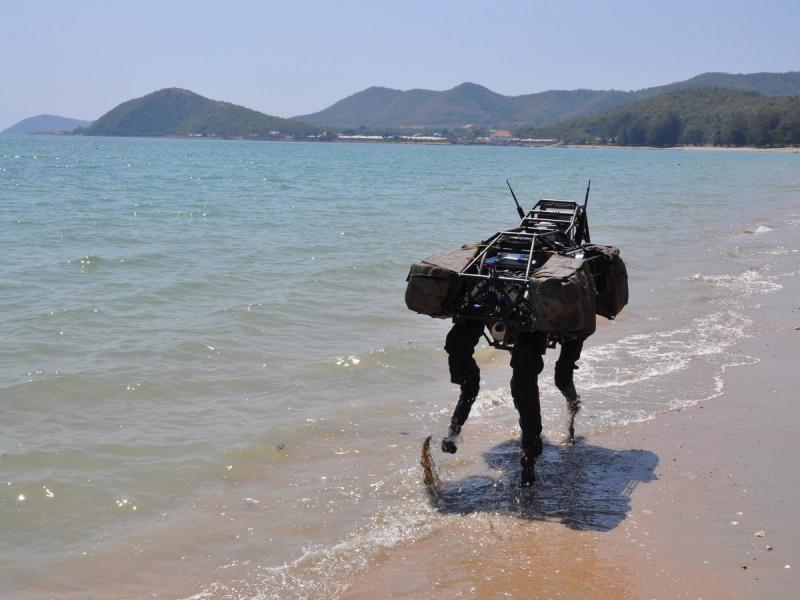
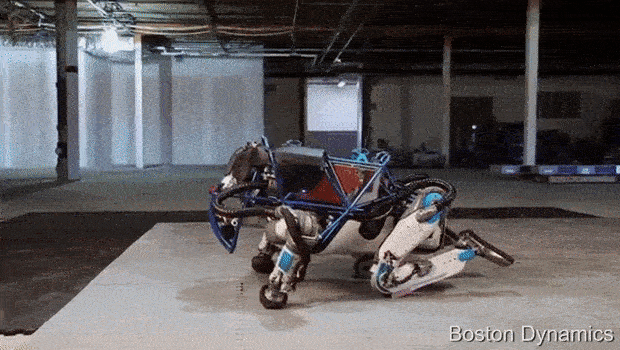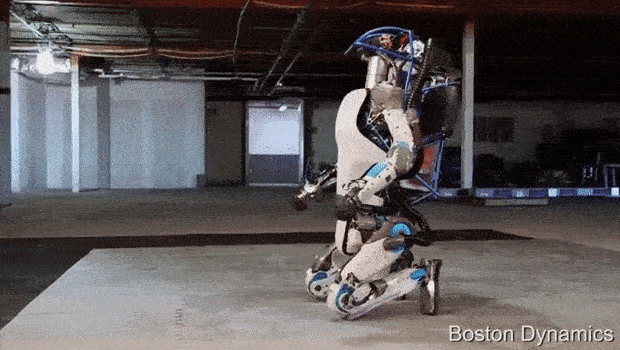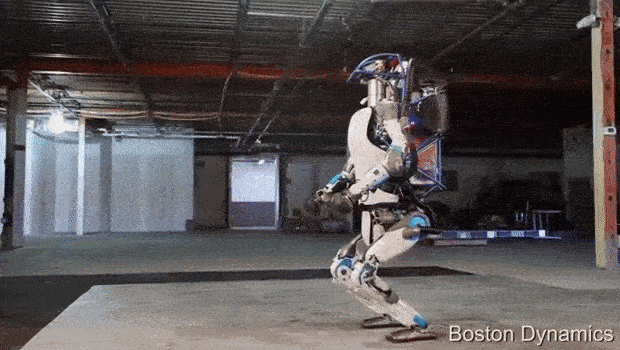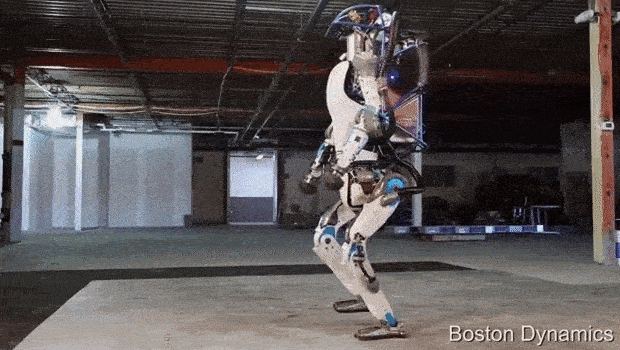
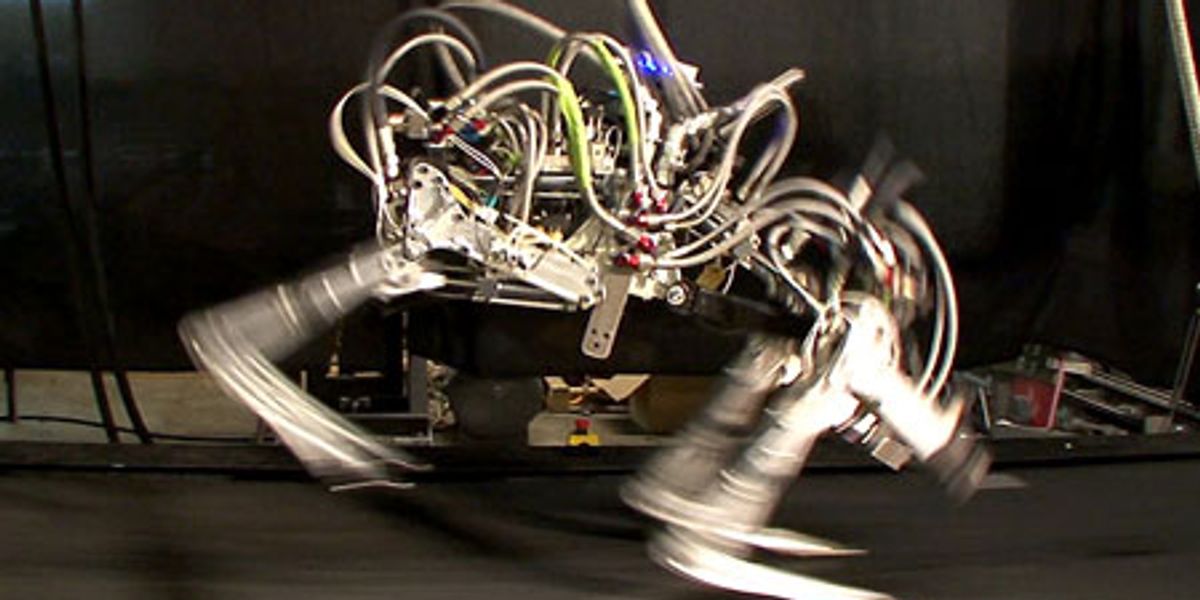
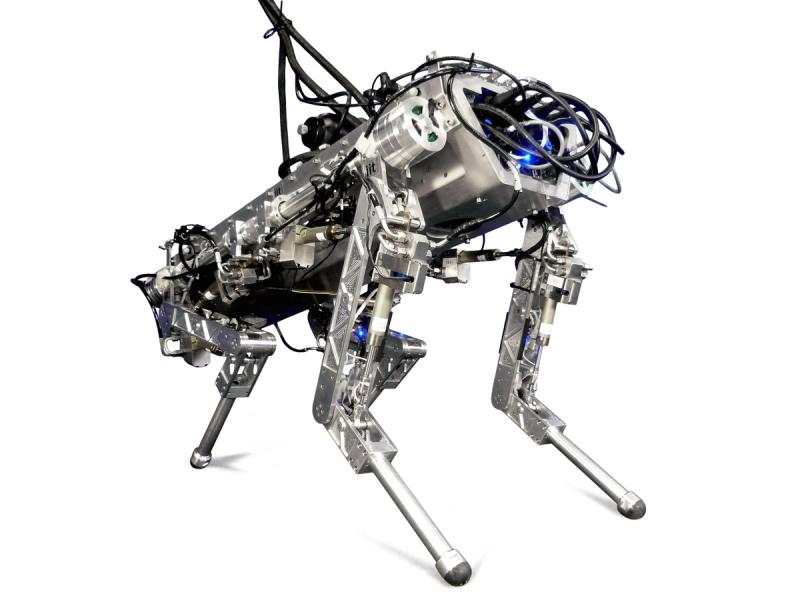
AlphaDog is a quadruped robot the size of a mule (a big mean mule). It's powered by a hydraulic actuation system and is designed to assist soldiers in carrying heavy gear over rough terrain.
- Creator
- Year
- 2011
- Country
- United States 🇺🇸
- Categories
- Features
More videos
Did you know?
AlphaDog was initially named "BullDog," but after realizing that the term evoked the image of cute dogs with droopy cheeks and pushed-in faces, Boston Dynamics decided against it.
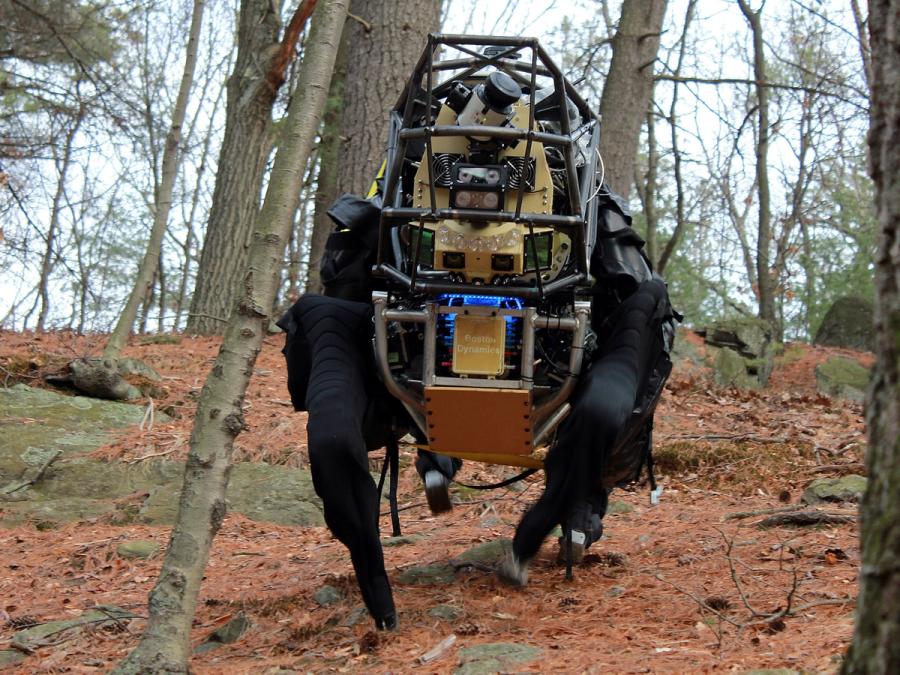

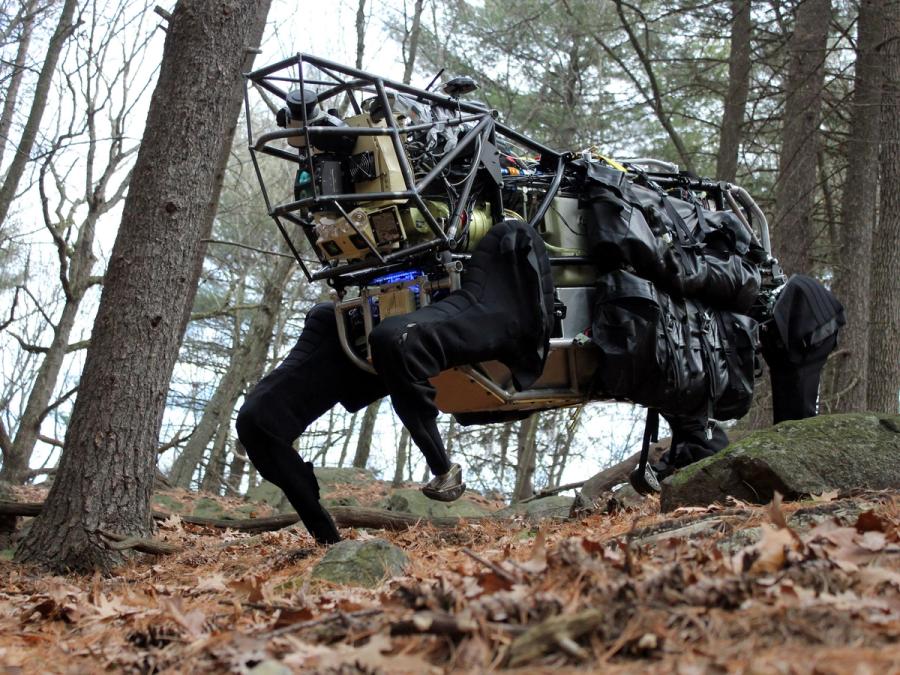
History
Boston Dynamics, led by Marc Raibert, was funded by DARPA and the U.S. Marine Corps. to develop a highly mobile, semi-autonomous legged robot, the Legged Squad Support System (LS3), to help alleviate physical weight on troops. In early 2012, the LS3 prototype underwent its first outdoor exercise, demonstrating the ability to follow a person using its vision system. Next DARPA plans to complete development of key mobile and sensing capabilities to ensure LS3 is able to support dismounted squads of soldiers in the battlefield. The team working on LS3 (also known as AlphaDog) includes engineers and scientists from Boston Dynamics, Bell Helicopter, AAI Corporation, Carnegie Mellon, NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, and Woodward HRT.
Specs
- Overview
Up to 181 kg (400 lb) of payload, dynamic locomotion over steep and slippery terrain.
- Status
Inactive
- Year
2011
- Website
- Width
- 90 cm
- Height
- 190 cm (fully extended legs)
- Length
- 200 cm
- Weight
- 362.9 kg
- Sensors
Legs with joint position and force sensors. Body with gyroscope and stereo vision system. Hydraulic system with pressure and temperature sensors.
- Actuators
Hydraulic actuators
- Degrees of Freedom (DoF)
- 12
- Compute
Custom PC
- Power
Internal combustion engine